Scouring is an important step in the pre-treatment process. It is a preparatory process that prepares the fabric for subsequent dyeing process. If scouring is not carried out properly, it will lead to uneven dyeing.If you want to know what is scouring and more information about it, you are on the right track. This article has the details on the Two Methods of Scouring Process in Textile Industry. Look no further! Let’s dive in…
What is scouring?
Scouring is a process in which the natural impurities of cellulosic fibers are normally removed by boiling off in a strong alkaline solution. The natural impurities such as mineral matters, oils, waxes, ashes hinder the penetration of dyes and chemicals to the interior of fiber which results in the huge wastage of dyes and chemicals. Again improper scouring leads to uneven dyeing. Alkali ( Caustic & soda Ash ) treatment with auxiliaries at high temperature removes the inherent and added impurities from cotton and other cellulosic fibers such as hemp, ramie, kenaf, linen, jute.
Reaction occurs during scouring
Raw cotton contains impurities in it and has a cuticle layer of pectins, oils or waxes around it which makes in quite hydrophobic. These are high molecular fatty acid such as steeric acid. During scouring process, concentrated caustic soda solution reacts with steeric acid by removing all these impurities and the goods become more absorbent.
Objectives of scouring
- Main purpose is to remove all impurities from the fabrics
- To make the fabric highly absorbent
- To facilitate dye and chemical penetration
- To remove non-cellulosic materials form cotton
- To leave the fabric in super absorptive state without any significant chemical or physical damage
- To improve the fabric handle
- To prepare the fabric for subsequent process
Impacts of scouring on cotton
- Saponification of oils and fatty acids leads to the conversion of water soluble soaps
- Proteins are hydrolyzed into water soluble amino acids or ammonia
- Pectin and pactose are solubilized and converted into soluble salts of pectic acid
- Extraction of mineral matter
- Unsaponifiable natural oils and waxes are emulsified
- Dirt particles are removed by detergent and alkali
- Dissolution of amino compounds
- Sizing materials are broken down.
Scouring depends on the following parameters
- Fabric construction
- Twist and count of yarn
- Fabric color
- Fabric type
- Cleanliness of fabric
Chemical requirement & their functions for scouring process
Based on the type and form of materials a series of chemicals are used in scouring bath. Usually, the scouring bath consists essentially of a caustic material and a surfactant, at least 0.01% by weight, based on the total weight of the scouring bath, of a solubilizing agent which is amino tri (methylene phosphonic acid). The key chemicals used for scouring process of different fibers and their functions are given below:
| Chemicals | Functions |
| Caustic Soda | · Neutralizes acidic materials · Saponify glycerides (waxes & oils) · Solubilizes silicate |
| Soda ash | · Neutralizes acidic materials · Saponify glycerides (waxes & oils) · Solubilizes silicate |
| Sodium silicate | · Penetrate & brake-down lignin in motes · These are added when fabric has large amount of motes and other assorted materials. |
| Surfactant | · Reduce surface tension · Reduce interfacial tension · Helps to wet out the materials with liquid |
| Detergents | · Emulsify fats, oils and waxes · Remove oil borne stains · Suspend materials after they have been removed |
| Sequestering agent | · Deactivate metal ions |
| Builder (salt) | · Cause detergents to become increasingly effective |
| Solvent | · Assists emulsification by dissolving oily materials |
A typical recipe for scouring:
| Chemicals used | Amounts needed |
| · Wetting agent · Detergent · Sequestering agent · Caustic soda (36°Be) · pH · M:L | · 0.5-1.0 g/L · 1.0-2.0 g/L · 1.0-3.0 g/L · 2.0-4.0 g/L · 10-11 · 1:10 |
Form of scouring
Scouring can be carried out both in yarn and fabric stage. Again, this process can be carried out in different forms. They are discussed below:
· Scouring of Yarn
Ø Hank form
Ø Package form
Ø Continuous warp sheet form
· Scouring of Fabric
Ø Open form: J-box, Pad-batch, Progressive Jigger
Ø Rope Form: Kier boiler, Washer
Scouring methods
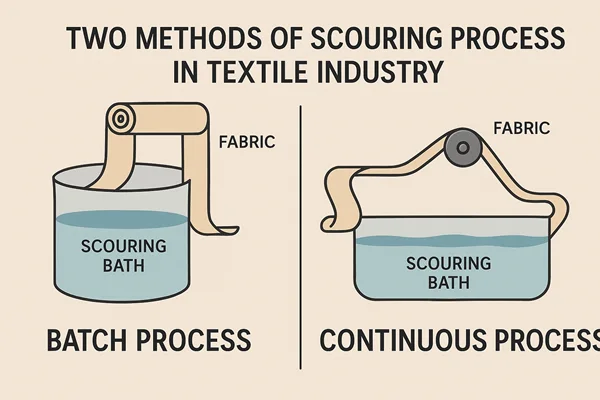
Scouring process is done mainly in two methods-
- Continuous process- In continuous process, fabric is scoured continuously in J-box where dyeing process is also carried out after pre-treatment. But in our industry, it has very limited use.
- Discontinuous Process- In this case, scouring is carried out in kier boiler, winch or jigger dyeing machine. As the name implies, it is carried out in discrete manner. Different lots or batches are created before dyeing. This process is also called Batch process.
Assessment of scouring
For estimation of scouring effect two types of methods can be carried out:
- Determination of weight loss
- Absorbency test
- Immersion test or Wicking test
Determination of weight loss
Absorbency test
- Drop test
Water is taken in a pipette and a drop of water is dropped on the scoured sample. Time for the absorption of that water drop is observed visually.
The standard time for absorption is 0.5-0.8 to 1 second.
- Spot test
1% direct or congo red solution is taken in a pipette. Then droplet of the solution is put on the different places of the scoured sample. The shape of the absorption area is then observed.
Wicking or Immersion test
- Sample preparation: 18cm × 5cm size sample is cut from the scoured sample. A mark is drawn above 1 cm from the sample bottom.
· Procedure:
Ø 1% direct red solution is taken in a pipette.
Ø Sample is hung from a wood-stick in such a way that 1 cm portion of that sample is immersed in the dye solution.
Ø Then the point up to which the solution is absorbed straight above the way in just 5 min.
· The standard range is 30-50 mm.
Difference between scouring & souring
- Don’t confuse with this two terms- Scouring and Souring. Both of the process are completely different from each other.
- Scouring is the process of removing impurities with strong alkali at boiling temperature.
- Whereas souring is the alkali neutralization process by using dilute acidic solution without any application of heat.
Main 2 types of scouring process
- Chemical or alkaline scouring- In this type, chemicals are used to conduct scouring process. This process need a lot of chemicals and not eco-friendly at all.
- Bio-scouring- this process use enzyme for scouring and completely eco-friendly process.
Bio-scouring
- Alkaline stable pectinase enzyme is used to remove pectin, wax or oil from the fabris.
- Bio-scouring is eco-friendly process
- Leave a soft handle on the fabric
- No core alkali neutralization is needed thus less washing cycle.
- Less TDS, COD, BOD
- Find out difference between bio-scouring and alkaline scouring.
Two Methods of Scouring Process in Textile Industry
Scouring is the process to remove natural and foreign impurities from the fabric and preparing the fabrics for the next subsequent process. This process makes the fabric hydrophilic so that it can absorb the chemicals and dyes properly. In this article, we will discuss the methods of the scouring process in Textile industry.
The non-continuous scouring process consists essentially of circulating hot alkali liquor through the cloth in a vessel called kier. The continuous scouring and bleaching in the J-Box have been established after 1960s. The continuous process is based on the impregnation of the fabric in an alkali solution followed by the steam aging stage, the fabric being either in rope form or open width form.
Kiers have given way to J-Boxes and J-Boxes are discarded in favor of open width scouring which requires only 2-15 min having very high production. In comparison, kiers take 6-12 h depending upon the number of impurities.
Two Methods of Scouring Process in Textile
There are two methods of scouring processes are available. They are described below:
- Continuous process: J-box machine
- Dis-continuous process: Kier boiler, Winch or Jigger machine
Batch Type or Discontinuous Process in Brief
Batch type or discontinuous scouring process in (rope form) are carried out in:
- Low pressure kier
- High pressure kier
- Jafferson-Walker’s kier
- Gebauer kier
Batch Type Scouring Machine (Open Width Form) is carried out in:
- Mather and Platt’s horizontal kier
- Jackson kier
- Jig process
Among all of these the most used process is high pressure kier boiler. In this article, we will cover this type of kier boiling method.
Machine Profile for Batch Process
- The prototype of a modern high pressure kier that has multi-tubular heater is often referred to as Walsh’s kier and considered to be the best.
- This machine is about 9 inch high and 6.5 inch in diameter with a 2 tons capacity.
- This machine is mounted on R.C.C columns.
- The maximum working pressure for this machine is 40 lb/in2 (2.812 kg/cm 2) at 141°C and is composed of mild steel plates with countersunk rivet heads inside to give a smooth surface.
- Various mountings and accessories like pressure gauge, safety valve, blow-off valves for air and steam, steam traps, liquor level indicators, and draincock are provided with this machine.
Recipe for Batch Process Scouring
| Chemicals | Amount needed |
| · Caustic soda · Soda ash · Wetting agent · Sequestering agent · Temperature · M:L | · 0.5-2.4 g/L · 0.5-1.0 g/L · 0.5-1.0 g/L · 0.5-1.0 g/L · 120-130°C · 1:100 |
Process Description
- On perforated false bottom the substrate needs to be plaited. No matter, it can be done either manually or mechanically.
- An alkaline solution is prepared that contains caustic soda (2 to 3%), sodium silicate (0.75 to 1%), sodium carbonate (0.5 to 1%) and wetting agent (0.1%) and the substrate is saturated in this solution at the time of piling.
- From the underside of kier, enough scouring liquor is introduced. Thus entrapped air is swept out to prohibit the oxy-cellulose formation.
- Then the lid is closed but the air valve is kept open.
- Turning on the steam, the liquor is circulated with the help of centrifugal pump.
- High pressure kier operates at about 130°C (2.109 kg/cm 2) for about 8 to 10 hours with a liquor ratio 5:1 to 6:1.
- After scouring the draincock is opened at reduced pressure (5 to 6 lb/in 2) and equivalent amount of hot water is admitted from the top.
- Once the cold water circulation on the goods is done, they are removed and transfer to the rope machine for washing.
- From the bottom of kier, the withdrawal of the liquor is carried out that is forced through the heater. A distributor is then used to spread over the substrate.
Fabric that is to sell at white state is given two boils whereas the fabrics intended for printing are given a single boil.
Advantages & Dis-Advantages of Batch Process
| Advantages | Dis-advantages |
| · Suitable for small orders · Fabric can be scoured in both open width and rope form. | · Not economical for large orders · Time requirement is more than continuous process |
Continuous Process in Brief
The continuous scouring process can be carried out by the following machines. A continuous process is rarely followed in the industry. But among all of these J-box machine is used mostly. So, we will cover j-box machine here.
- Saturator- J-Box-rope washer
- Open width roller steamer
- Vaporloc system
- High pressure Klienewefer roller steamer
- Conveyer storage steamer system
- Roller bed steamer with pre-swelling zone
Saturator- J-Box- rope washer
This procedure can be divided into 4 stages:
- Saturator
- Pre-heater
- J-box
- Washing unit
Recipe for Continuous Process
| Chemicals | Amount needed |
| · Caustic soda · Wetting agent · Sequestering agent · Impregnation temperature · Storing time in J-box · J-box temperature | · 5 g/L · 1-4.5 g/L · 1-5 g/L · 70-80°C · 8-10 min (open width form) 40-60 min (rope form) · 100-105°C |
Process Description of Continuous Process
- Saturator: If you are thinking about continuous machine, a series of j-box can be used for scouring or desizing. The desized and washed cloth is first saturated with scouring solution at about 70-80°C in a saturator.
- Pre-heater: The cloth before entering J-Box is rapidly pre-heated by means of steam in a U-shaped heating tube. Where the temperature range is 110-120°C. In case of Becco system, there is no pre-heater and the cloth is directly heated in the J-Box which is used as a steamer
- J-box:
- Once the padding is completed, the substarte passes through the pre-heater. Then it enters into Du Pont type J-Box and kept for 40-60 min in plaited form at 100°C.
- No friction occurs on the moving substrate. This is so because the internal area of the j-box is very smooth.
- In-stead of rope form a multi-stage J-Box in open width form can also be used with a dwell time of 8-10 min in J-Box.
Washing unit: The scoured fabric is washed outside heaving a counter current arrangement at the temperature of about 70-80°C.
Advantages & Dis-Advantages of Continuous Process
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| · Fabric is scoured in both open width and rope form. · Suitable for large orders · Less time required | · Not economical for large orders |
Wrapping It Up!
Scouring is a must procedure that should be carried out in the case of natural fibers. Otherwise, proper dyeing can’t be possible. Without scouring, no wax or foreign materials won’t come off from natural fibers and that will lead to patchy dyeing.Without pre-treatment, dyeing process can’t be carried out. Scouring helps in proper dyeing process. In our textile industry, scouring is a must.
- You May love to read: Scouring Process in Textile Industry.
- General Recipe for Scouring and Bleaching of Knitted Fabric
- Bio-Scouring Process: A Sustainable Bio-Scouring Process for Better Fabric Dyeing


