A dispersant or dispersing agent makes the dispersion process more stable and easier for a solid material dispersed in a liquid. The dispersing agent has an effect on the rate of dyeing. It increases the solubility of the disperse dye as well as increases the dyeing rate up to a certain time. But after that certain value, the rate of dyeing decreases with the addition of disperse dye. In this article, we are discussing Functions and the Effect of dispersing agents in the Dyeing Process.
Dispersing agents are stable under dyeing conditions. They are significantly resistant to hard water, high temperature even at other dyeing auxiliaries. They help to maintain the dye molecule dispersion in the dye bath. Disperse dyes remain in an aggregated form, which is not suitable for the application on hydrophobic fibers.
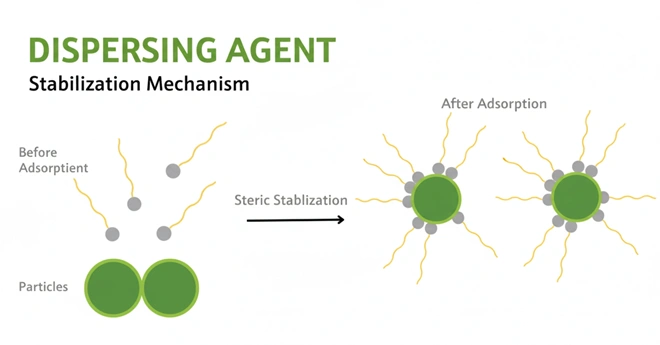
If they remain in an aggregated form, they will produce uneven and speckled shades. So, a dispersing agent is required to produce a stable formulation and to ensure storage stability (No viscosity instability, no separation). It helps to distribute the solid dye particles in a liquid solution.
Functions of the dispersing agent
- It helps to reduce the particle size of the dye
- Enables the formation of dye powder form
- For carrying out dyeing, it helps in the re-conversion process of dye powder into a dispersion
- Maintains the dispersion of dye in fine form during the whole dyeing process
- Having no wetting, foaming, or detergent properties
- Increases the solubility of the Disperse dye
- It has an impact on the rate of dyeing
- Shows compatibility with anionic and non-ionic products
Disperse dye dispersion with a dispersing agent
Disperse dyes are available as powders, grains, pastes, or aqueous dispersions. Dyes contain micro-fine dye particles with a diameter below 1 µm. These cause the variation in the amount of dispersing agent.
- Dispersing agent coats the surface of each dye particle with a monomolecular layer of adsorbed dispersant.
Since these chemicals are invariably anionic polymers, the more hydrophobic sections of the polymer chain adsorb onto the hydrophobic dye particle surface with the anionic groups of the polymer exposed to the surrounding water.
The overall negative charge on the surface of each particle prevents their coalescence and aggregation. - The original dispersant was sulphated ricinoleic acid. Modern dispersants are often either lignosulphonates from paper pulping, sulphonates of alkylnaphthaleneformaldehyde condensates or sodium oleyl-p-anisidide sulphonate.
- The presence of a dispersing agent in the dye bath increases the apparent water solubility of the dye.
- The rate of solution of the dye does not control the overall rate of dyeing as the dyes consist of very small particles to give the maximum specific surface area.
The average particle size will gradually increase during dyeing as the smaller particles dissolve more rapidly. The very fine state of division avoids dye specks on the goods. - Dispersions may not always be stable under the dyeing conditions. It may occur in the Jet and Package machine, which involves high temperatures and high shear forces.
The dye bath usually contains an additional dispersant to maintain the dispersion of the dye and to promote levelling. This is more important for pale shades when the amount of dispersant added from the dye powder or liquid is low.
Effect of dispersing agent on the rate of dyeing
- It is seen from the above figure that the dyeing rate increases with increasing solubility up to a certain value, and with further increase in solubility, the dyeing rate actually decreases. Where the solubility is very high, as in the case of direct dyes, practically no dyeing takes place.
- If the dye has fairly low solubility, say OA, the addition of a dispersing agent raises the solubility to OB so that the dyeing rate increases from AP to BQ.
- If the dye has fairly high solubility (OB), the addition of the dispersing agent may increase it further, say to OD. In this case, the dyeing rate is actually decreased from BQ to DS.
Trade names of dispersing agents
| Name of product | Name of Company |
| Dispersant WS | Indokem Ltd. |
| Polydisperse WS | 3-Silicon and Chemicals Pvt. Ltd. |
| Dispersing agent NS | Ultra Color Corporation |
| Luckokem AK | Keumicolor Industries |
| Dispervat 60 | Sri Ambja Chemicals |
| Setamol WS | BASF India |
| Dadamol V | Dyes and Dispersing agent Pvt. Ltd. |
| Pidimol TD | Parekg Dyechem industries Pvt. Ltd. |
| Sarcol NS | Gujchem Distillers India Ltd. |
| Lycol OL | Sandoz (India) |
| Eldon | Sandoz |
| Nitamol NV-50 | New India Trading Corporation |
Examples of dispersing agents
- Soap powder
- Lignin sulphonates
- Turkey red oil
- Formaldehyde
- Alkyl acryl sulphonates
To Wrap Up!
The dispersing agent plays an important role in the dyeing of polyester with disperse dye. It helps in dyeing by increasing the solubility of the disperse dye, along with an increase in the dyeing rate up to a certain time.


