Color plays a crucial role in our lives, influencing our moods, emotions, and overall perception of the world. In the textile industry, color holds immense significance as it has the power to transform a piece of fabric into a captivating masterpiece. The understanding and application of color theory in textile design not only stimulate creativity but also drive market appeal. By employing the principles of color theory, textile professionals can create visually appealing products that resonate with consumer preferences. This article delves into the Understanding of Fundamentals principles and the importance of color theory in textile design and its impact on design, aesthetics, and market success.
Understanding Color Theory
Color theory is a system of principles that explains how colors interact and influence each other when combined or placed in proximity. It encompasses various elements, including the color wheel, color harmony, contrast, and the psychology of color. By understanding these fundamental concepts, textile designers can create harmonious and visually pleasing compositions.
Understanding color theory is essential for professionals in the textile industry as it forms the basis for effective textile design. By grasping the principles of color theory, textile designers can create visually appealing and harmonious compositions that resonate with consumers. Let’s explore some key aspects of color theory in the context of the textile industry.
What are the 8 Fundamental Principles of Color Theory
- Color Wheel
- Color Harmony
- Contrast
- Color Psychology
- Cultural and Market Considerations
- Material and Application
- Personal Style and Brand Identity
- Color Trends and Forecasting
Description of Fundamental Principles of Color Theory for Textile Design
The Color Wheel

The color wheel is a visual representation of the primary, secondary, and tertiary colors and their relationship to each other. It serves as a foundation for understanding color relationships and creating harmonious combinations. Textile designers can use the color wheel to identify complementary, analogous, and triadic color schemes, which can enhance the visual impact of their creations.
Color Harmony
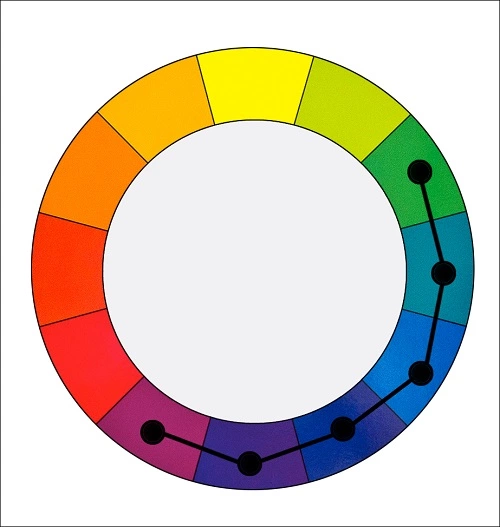
Color harmony refers to the pleasing arrangement of colors in a design. Achieving harmony involves understanding the relationships between colors, such as complementary colors (opposites on the color wheel), analogous colors (adjacent on the color wheel), and triadic colors (equidistant on the color wheel). Textile designers can leverage these harmonious combinations to create balanced and visually engaging textile patterns and motifs.
Contrast: Adding Depth and Visual Interest
Contrast is a powerful tool in textile design that involves the juxtaposition of colors with significant differences in value, hue, or intensity. By using contrasting colors effectively, designers can add depth and visual interest to their textile creations. Contrast can be achieved through complementary colors, light-dark variations, or by combining warm and cool tones. It helps highlight specific design elements and draw attention to intricate details, making textiles more appealing to consumers.
Color Psychology
Colors have the ability to evoke emotions and influence our perceptions. Understanding the psychology of color is essential for textile designers as it helps them create products that align with the desired mood or message. For example, vibrant and warm colors like red and orange can convey energy and excitement, while cooler tones such as blue and green evoke feelings of calmness and serenity. By strategically employing colors based on their psychological impact, textile designers can elicit specific emotional responses from consumers.
Cultural and Market Considerations
In the textile industry, it is important to consider cultural preferences and market trends when selecting colors for designs. Different cultures associate specific meanings and symbolism with colors, so designers need to be mindful of these cultural nuances to avoid any unintended messages or associations. Additionally, staying abreast of current market trends and consumer preferences in terms of color choices is essential for creating textiles that appeal to the target audience.
In the highly competitive textile industry, understanding consumer preferences and market trends is vital for success. Color has a significant impact on consumer buying behavior, as it can evoke strong emotions and influence purchasing decisions.
Material and Application
The choice of colors in textile design should also consider the material and intended application of the fabric. Certain colors may work better on specific materials, while others may be more suitable for particular end uses. Textile designers should consider factors such as fabric dyeability, colorfastness, and the desired aesthetic effect when selecting colors for their designs.
Personal Style and Brand Identity
Colors can become synonymous with a brand or individual’s identity, providing a visual language that sets them apart. Textile designers can utilize color theory to develop a unique and recognizable aesthetic for their brand or clients. Consistency in color usage across different textile collections helps establish a cohesive brand identity, making it easier for consumers to recognize and connect with the brand.
Color Trends and Forecasting
Color trends play a crucial role in the textile industry, shaping consumer preferences and influencing market demand. By keeping a pulse on the latest color trends and forecasting future color palettes, textile designers can stay ahead of the curve and design products that align with them.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a solid understanding of color theory is vital for success in the textile industry. By utilizing the principles of color theory, textile designers can create harmonious, visually engaging, and marketable textile products that resonate with consumers. The thoughtful application of color theory helps designers make informed decisions, evoke desired emotions, establish brand identities, and stay ahead of market trends, ultimately enhancing the overall quality and appeal of their textile creations.
By applying color theory principles, textile designers can create products that resonate with the target audience, leading to increased market appeal and customer satisfaction.
- You may Love to read: Application of Pantone for Color Evaluation in Textile and Apparel
- Use of Lightbox in Textile and Apparel Industry
